Site Blog
contact us
- If you have questions, please contact us, all questions will be answered
- Email : David@tmaxcn.com
- Email : Davidtmaxcn@gmail.com
- Add : No. 39, Xinchang Road, Xinyang, Haicang Dist., Xiamen, Fujian, China (Mainland)
hot products
Blog
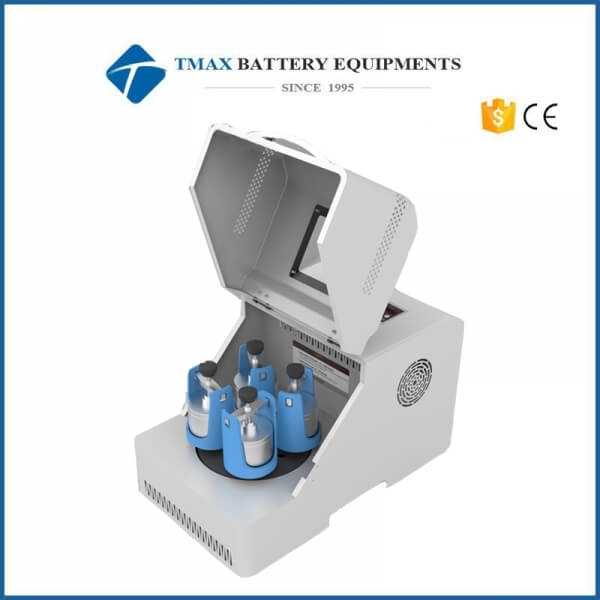
Ball Mill Grinder
A ball mill grinder is a widely used grinding machine designed to reduce materials into fine powders or particles. It operates by rotating a cylindrical chamber filled with grinding media (typically steel balls) and the material to be ground. As the cylinder rotates, the grinding media collide with the material, breaking it down into smaller sizes through impact and attrition.
In this article, we will explore the principles, design, applications, advantages, challenges, and innovations associated with ball mill grinders.
●Principles of Operation
1. Mechanism
The ball mill consists of a horizontal cylindrical chamber that rotates around its axis.
Inside the chamber, grinding media (e.g., steel balls, ceramic balls, or other materials) are mixed with the raw material.
As the cylinder rotates, the grinding media lift and cascade, creating repeated impacts and friction against the material, reducing it to fine particles.
2. Key Parameters
Rotation Speed: Determines the energy imparted to the grinding media and affects particle size distribution.
Grinding Media Size: Smaller media produce finer particles, while larger media are better for coarse grinding.
Material Feed Rate: Controls the throughput and ensures uniform processing.
Chamber Dimensions: Larger chambers allow for higher capacity but may require more energy.
●Design of Ball Mill Grinders
1. Cylindrical Chamber
Made of durable materials like steel or rubberlined steel to withstand wear and tear.
Can be designed for batch or continuous operation.
2. Grinding Media
Typically made of steel, ceramic, or other hard materials depending on the application.
The choice of media depends on factors like abrasiveness of the material and desired particle size.
3. Drive System
Provides controlled rotation of the cylinder at optimal speeds for efficient grinding.
4. Feed and Discharge Systems
Ensures smooth feeding of raw material into the chamber and removal of processed material.
5. Cooling System
Prevents overheating during prolonged operation, especially in highenergy grinding processes.
●Advantages of Ball Mill Grinders
1. Versatility
Suitable for grinding a wide range of materials, including metals, minerals, ceramics, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals.
2. Uniform Particle Size
Produces consistent and fine particle sizes, which is critical for many industrial applications.
3. Scalability
Available in various sizes, from laboratoryscale units to large industrial machines.
4. Durability
Designed to handle abrasive and hard materials without significant wear.
5. Customizable
Adjustable parameters (e.g., speed, media size, and chamber dimensions) allow optimization for specific applications.
●Challenges in Using Ball Mill Grinders
1. Energy Consumption
High energy requirements, especially for fine grinding applications.
2. Noise Levels
Generates significant noise during operation, requiring soundproofing measures.
3. Wear and Tear
Frequent replacement of grinding media and chamber lining due to abrasion.
4. Contamination
Steel grinding media can introduce metallic impurities into the material, which may be undesirable in certain applications.
5. Complexity
Proper setup and maintenance require technical expertise.
●Types of Ball Mill Grinders
1. Batch Ball Mills
Process a fixed amount of material at a time.
Suitable for smallscale operations or when precise control over grinding conditions is required.
2. Continuous Ball Mills
Allow continuous feeding and discharge of material.
Ideal for largescale industrial applications.
3. Planetary Ball Mills
Use multiple grinding jars that rotate around their own axes and a central axis simultaneously.
Provide highenergy grinding for ultrafine particles.
4. Attrition Mills
Combine the principles of ball mills and stirred mills for faster and more efficient grinding.
5. Vibration Ball Mills
Utilize highfrequency vibrations to enhance grinding efficiency and achieve finer particle sizes.
●Applications of Ball Mill Grinders
Ball mill grinders are employed across various industries for diverse applications:
1. Mining and Mineral Processing
Grinding ores and minerals for extraction and purification processes.
2. Ceramics
Producing fine powders for manufacturing ceramics, glazes, and pigments.
3. Chemical Industry
Mixing and grinding chemicals for reactions or formulation.
4. Pharmaceuticals
Creating uniform particle sizes for drug formulations and active ingredients.
5. Construction Materials
Grinding cement, limestone, and other building materials.
6. Metallurgy
Preparing metal powders for sintering or alloy production.
7. Food Industry
Grinding spices, grains, and other food products for consistent texture.
●Innovations in Ball Mill Grinder Technology
To address the challenges and enhance performance, manufacturers are incorporating cuttingedge technologies:
1. Advanced Materials
Using wearresistant coatings and ceramics for longerlasting components.
2. Automated Control Systems
Programmable controls for optimizing grinding parameters and reducing human intervention.
3. Energy Efficiency
Improved designs and drive systems to reduce energy consumption.
4. RealTime Monitoring
Sensors and data analytics tools to monitor grinding efficiency and particle size distribution.
5. EcoFriendly Solutions
Developing ball mills with reduced noise levels and lower environmental impact.
●The Future of Ball Mill Grinder Technology
As material processing demands continue to evolve, so too will the technology behind ball mill grinders. Key trends shaping the future include:
1. Increased Automation
Fully autonomous systems for streamlined operation and maintenance.
2. Focus on Sustainability
Energyefficient designs and ecofriendly materials to minimize environmental impact.
3. Integration with Emerging Technologies
Combining ball mills with AI, IoT, and cloud computing for smarter diagnostics and analysis.
4. Development of New Materials
Adapting ball mills for advanced materials like nanomaterials and composites.
5. Global Standards Compliance
Ensuring compatibility with evolving international regulations for material processing.
●Conclusion
Ball mill grinders are a powerful and versatile tool for reducing materials into fine powders across a wide range of industries. Their ability to achieve uniform particle sizes and handle diverse materials makes them indispensable in modern manufacturing processes.
January 16,2026.
Xiamen Tmax Battery Equipments Limited was set up as a manufacturer in 1995, dealing with lithium battery equipments, technology, etc. We have total manufacturing facilities of around 200000 square foot and more than 230 staff. Owning a group of experie-nced engineers and staffs, we can bring you not only reliable products and technology, but also excellent services and real value you will expect and enjoy.
A ball mill grinder is a widely used grinding machine designed to reduce materials into fine powders or particles. It operates by rotating a cylindrical chamber filled with grinding media (typically steel balls) and the material to be ground. As the cylinder rotates, the grinding media collide with the material, breaking it down into smaller sizes through impact and attrition.
In this article, we will explore the principles, design, applications, advantages, challenges, and innovations associated with ball mill grinders.
●Principles of Operation
1. Mechanism
The ball mill consists of a horizontal cylindrical chamber that rotates around its axis.
Inside the chamber, grinding media (e.g., steel balls, ceramic balls, or other materials) are mixed with the raw material.
As the cylinder rotates, the grinding media lift and cascade, creating repeated impacts and friction against the material, reducing it to fine particles.
2. Key Parameters
Rotation Speed: Determines the energy imparted to the grinding media and affects particle size distribution.
Grinding Media Size: Smaller media produce finer particles, while larger media are better for coarse grinding.
Material Feed Rate: Controls the throughput and ensures uniform processing.
Chamber Dimensions: Larger chambers allow for higher capacity but may require more energy.
●Design of Ball Mill Grinders
1. Cylindrical Chamber
Made of durable materials like steel or rubberlined steel to withstand wear and tear.
Can be designed for batch or continuous operation.
2. Grinding Media
Typically made of steel, ceramic, or other hard materials depending on the application.
The choice of media depends on factors like abrasiveness of the material and desired particle size.
3. Drive System
Provides controlled rotation of the cylinder at optimal speeds for efficient grinding.
4. Feed and Discharge Systems
Ensures smooth feeding of raw material into the chamber and removal of processed material.
5. Cooling System
Prevents overheating during prolonged operation, especially in highenergy grinding processes.
●Advantages of Ball Mill Grinders
1. Versatility
Suitable for grinding a wide range of materials, including metals, minerals, ceramics, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals.
2. Uniform Particle Size
Produces consistent and fine particle sizes, which is critical for many industrial applications.
3. Scalability
Available in various sizes, from laboratoryscale units to large industrial machines.
4. Durability
Designed to handle abrasive and hard materials without significant wear.
5. Customizable
Adjustable parameters (e.g., speed, media size, and chamber dimensions) allow optimization for specific applications.
●Challenges in Using Ball Mill Grinders
1. Energy Consumption
High energy requirements, especially for fine grinding applications.
2. Noise Levels
Generates significant noise during operation, requiring soundproofing measures.
3. Wear and Tear
Frequent replacement of grinding media and chamber lining due to abrasion.
4. Contamination
Steel grinding media can introduce metallic impurities into the material, which may be undesirable in certain applications.
5. Complexity
Proper setup and maintenance require technical expertise.
●Types of Ball Mill Grinders
1. Batch Ball Mills
Process a fixed amount of material at a time.
Suitable for smallscale operations or when precise control over grinding conditions is required.
2. Continuous Ball Mills
Allow continuous feeding and discharge of material.
Ideal for largescale industrial applications.
3. Planetary Ball Mills
Use multiple grinding jars that rotate around their own axes and a central axis simultaneously.
Provide highenergy grinding for ultrafine particles.
4. Attrition Mills
Combine the principles of ball mills and stirred mills for faster and more efficient grinding.
5. Vibration Ball Mills
Utilize highfrequency vibrations to enhance grinding efficiency and achieve finer particle sizes.
●Applications of Ball Mill Grinders
Ball mill grinders are employed across various industries for diverse applications:
1. Mining and Mineral Processing
Grinding ores and minerals for extraction and purification processes.
2. Ceramics
Producing fine powders for manufacturing ceramics, glazes, and pigments.
3. Chemical Industry
Mixing and grinding chemicals for reactions or formulation.
4. Pharmaceuticals
Creating uniform particle sizes for drug formulations and active ingredients.
5. Construction Materials
Grinding cement, limestone, and other building materials.
6. Metallurgy
Preparing metal powders for sintering or alloy production.
7. Food Industry
Grinding spices, grains, and other food products for consistent texture.
●Innovations in Ball Mill Grinder Technology
To address the challenges and enhance performance, manufacturers are incorporating cuttingedge technologies:
1. Advanced Materials
Using wearresistant coatings and ceramics for longerlasting components.
2. Automated Control Systems
Programmable controls for optimizing grinding parameters and reducing human intervention.
3. Energy Efficiency
Improved designs and drive systems to reduce energy consumption.
4. RealTime Monitoring
Sensors and data analytics tools to monitor grinding efficiency and particle size distribution.
5. EcoFriendly Solutions
Developing ball mills with reduced noise levels and lower environmental impact.
●The Future of Ball Mill Grinder Technology
As material processing demands continue to evolve, so too will the technology behind ball mill grinders. Key trends shaping the future include:
1. Increased Automation
Fully autonomous systems for streamlined operation and maintenance.
2. Focus on Sustainability
Energyefficient designs and ecofriendly materials to minimize environmental impact.
3. Integration with Emerging Technologies
Combining ball mills with AI, IoT, and cloud computing for smarter diagnostics and analysis.
4. Development of New Materials
Adapting ball mills for advanced materials like nanomaterials and composites.
5. Global Standards Compliance
Ensuring compatibility with evolving international regulations for material processing.
●Conclusion
Ball mill grinders are a powerful and versatile tool for reducing materials into fine powders across a wide range of industries. Their ability to achieve uniform particle sizes and handle diverse materials makes them indispensable in modern manufacturing processes.
What excites you most about the advancements in ball mill grinder technology? Share your thoughts below! Together, let’s explore how these innovative machines can shape the future of material processing and sustainability.
 English▼
English▼





 +86 13174506016
+86 13174506016 David@tmaxcn.com
David@tmaxcn.com

