Site Blog
contact us
- If you have questions, please contact us, all questions will be answered
- Email : David@tmaxcn.com
- Email : Davidtmaxcn@gmail.com
- Add : No. 39, Xinchang Road, Xinyang, Haicang Dist., Xiamen, Fujian, China (Mainland)
hot products
Blog
Battery Separator
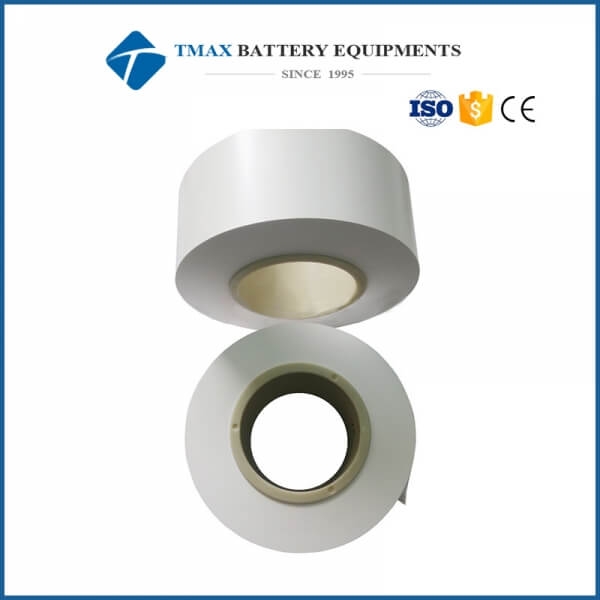
A battery separator is a thin, porous membrane placed between the positive and negative electrodes in a battery. Its primary function is to prevent direct electrical contact between the electrodes while allowing the free movement of ions through the electrolyte. This ensures safe and efficient electrochemical reactions within the battery. The separator plays a vital role in determining the performance, safety, and lifespan of a battery.
In this article, we will explore the properties, types, functions, advantages, challenges, and innovations associated with battery separators.
●Functions of a Battery Separator
1. Electrical Insulation
Prevents short circuits by physically separating the anode and cathode.
2. Ion Conduction
Allows the flow of ions (e.g., lithium ions in Liion batteries) through the electrolyte, enabling the electrochemical reactions necessary for charging and discharging.
3. Thermal Stability
Maintains structural integrity at high temperatures to prevent thermal runaway, a critical safety feature in modern batteries.
4. Mechanical Support
Provides structural support to the battery cell, especially during manufacturing and cycling.
5. Chemical Compatibility
Resists chemical degradation from the electrolyte and other battery components over time.
●Properties of Battery Separators
To perform effectively, battery separators must possess the following key properties:
1. High Porosity
Ensures efficient ion transport while maintaining mechanical strength.
2. Low Thickness
Reduces internal resistance and increases energy density by maximizing active material volume.
3. Chemical Inertness
Remains stable under harsh conditions, such as high voltages, temperatures, and exposure to reactive chemicals.
4. Thermal Resistance
Retains its structure and functionality even at elevated temperatures.
5. Puncture Resistance
Prevents internal shorts caused by dendrite growth or physical damage.
●Types of Battery Separators
1. Polymeric Separators
Made from materials like polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), or their combinations.
Widely used in lithiumion batteries due to their excellent mechanical strength, thermal stability, and low cost.
Some polymeric separators include shutdown features that melt and close pores at high temperatures to prevent overheating.
2. CeramicCoated Separators
Polymeric separators coated with ceramic particles (e.g., alumina or boehmite).
Enhance thermal stability, puncture resistance, and wettability by the electrolyte.
Commonly used in highpower and highsafety applications.
3. Glass Fiber Separators
Made from woven or nonwoven glass fibers.
Used primarily in leadacid batteries for their excellent chemical resistance and dimensional stability.
4. Composite Separators
Combine multiple materials (e.g., polymers, ceramics, and nanomaterials) to achieve superior performance.
Offer enhanced thermal stability, mechanical strength, and ion conductivity.
5. NanomaterialBased Separators
Incorporate graphene, carbon nanotubes, or other nanomaterials to improve ion transport and mechanical properties.
Emerging technology for nextgeneration batteries.
●Advantages of Battery Separators
1. Safety Enhancement
Prevents short circuits and thermal runaway, ensuring safe operation.
2. Improved Performance
Optimizes ion transport and reduces internal resistance, leading to better efficiency.
3. Longevity
Protects the electrodes from degradation, extending the battery's lifespan.
4. Versatility
Suitable for various battery chemistries, including lithiumion, nickelmetal hydride (NiMH), and leadacid.
5. CostEffectiveness
Mass production of polymeric separators makes them affordable for widespread use.
●Challenges in Battery Separator Technology
1. Thermal Management
High temperatures can cause shrinkage or melting of some separators, leading to failure.
2. Dendrite Growth
Lithium dendrites can penetrate the separator, causing internal shorts and safety hazards.
3. Wettability
Poor wettability by the electrolyte can hinder ion transport and reduce performance.
4. Environmental Impact
Disposal of nonbiodegradable separators poses environmental concerns.
5. Manufacturing Complexity
Producing advanced separators with uniform porosity and thickness can be challenging.
●Innovations in Battery Separator Technology
To address these challenges and enhance performance, researchers and manufacturers are developing cuttingedge separator technologies:
1. Smart Separators
Incorporate sensors to monitor temperature, pressure, and other parameters in realtime for predictive maintenance.
2. SelfHealing Materials
Use polymers or nanomaterials capable of repairing small defects to prevent catastrophic failures.
3. GrapheneBased Separators
Leverage graphene's exceptional mechanical strength and conductivity to create ultrathin, highperformance separators.
4. Biodegradable Materials
Develop environmentally friendly separators made from natural or renewable resources.
5. SolidState Separators
Explore solid electrolytes as alternatives to liquidbased separators for safer and more energydense batteries.
●Applications of Battery Separators
Battery separators are used across a wide range of industries and applications:
1. Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Ensure safe and efficient operation of highcapacity lithiumion batteries in EVs.
2. Consumer Electronics
Enable compact and reliable batteries for smartphones, laptops, and other portable devices.
3. Renewable Energy Systems
Facilitate energy storage in solar panels, wind turbines, and gridscale systems.
4. Medical Devices
Power implantable devices and diagnostic equipment where reliability and safety are paramount.
5. Industrial Applications
Support heavyduty batteries for backup power, telecommunications, and transportation.
●The Future of Battery Separator Technology
As battery technology continues to evolve, so too will the separators that enable their performance. Key trends shaping the future include:
1. Increased Efficiency
Development of thinner, more conductive separators to maximize energy density.
2. Focus on Safety
Enhanced thermal stability and puncture resistance to prevent catastrophic failures.
3. Integration with Emerging Technologies
Combining separators with solidstate electrolytes and nanomaterials for nextgeneration batteries.
4. Sustainability
Greater emphasis on using biodegradable and recyclable materials to reduce environmental impact.
5. Global Standards Compliance
Ensuring compatibility with evolving international regulations for battery components.
●Conclusion
Battery separators are a critical component in modern energy storage systems, ensuring safe and efficient electrochemical reactions. Their unique combination of electrical insulation, ion conduction, and mechanical strength makes them indispensable in a wide range of applications.
January 13,2026.
Xiamen Tmax Battery Equipments Limited was set up as a manufacturer in 1995, dealing with lithium battery equipments, technology, etc. We have total manufacturing facilities of around 200000 square foot and more than 230 staff. Owning a group of experie-nced engineers and staffs, we can bring you not only reliable products and technology, but also excellent services and real value you will expect and enjoy.
A battery separator is a thin, porous membrane placed between the positive and negative electrodes in a battery. Its primary function is to prevent direct electrical contact between the electrodes while allowing the free movement of ions through the electrolyte. This ensures safe and efficient electrochemical reactions within the battery. The separator plays a vital role in determining the performance, safety, and lifespan of a battery.
In this article, we will explore the properties, types, functions, advantages, challenges, and innovations associated with battery separators.
●Functions of a Battery Separator
1. Electrical Insulation
Prevents short circuits by physically separating the anode and cathode.
2. Ion Conduction
Allows the flow of ions (e.g., lithium ions in Liion batteries) through the electrolyte, enabling the electrochemical reactions necessary for charging and discharging.
3. Thermal Stability
Maintains structural integrity at high temperatures to prevent thermal runaway, a critical safety feature in modern batteries.
4. Mechanical Support
Provides structural support to the battery cell, especially during manufacturing and cycling.
5. Chemical Compatibility
Resists chemical degradation from the electrolyte and other battery components over time.
●Properties of Battery Separators
To perform effectively, battery separators must possess the following key properties:
1. High Porosity
Ensures efficient ion transport while maintaining mechanical strength.
2. Low Thickness
Reduces internal resistance and increases energy density by maximizing active material volume.
3. Chemical Inertness
Remains stable under harsh conditions, such as high voltages, temperatures, and exposure to reactive chemicals.
4. Thermal Resistance
Retains its structure and functionality even at elevated temperatures.
5. Puncture Resistance
Prevents internal shorts caused by dendrite growth or physical damage.
●Types of Battery Separators
1. Polymeric Separators
Made from materials like polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), or their combinations.
Widely used in lithiumion batteries due to their excellent mechanical strength, thermal stability, and low cost.
Some polymeric separators include shutdown features that melt and close pores at high temperatures to prevent overheating.
2. CeramicCoated Separators
Polymeric separators coated with ceramic particles (e.g., alumina or boehmite).
Enhance thermal stability, puncture resistance, and wettability by the electrolyte.
Commonly used in highpower and highsafety applications.
3. Glass Fiber Separators
Made from woven or nonwoven glass fibers.
Used primarily in leadacid batteries for their excellent chemical resistance and dimensional stability.
4. Composite Separators
Combine multiple materials (e.g., polymers, ceramics, and nanomaterials) to achieve superior performance.
Offer enhanced thermal stability, mechanical strength, and ion conductivity.
5. NanomaterialBased Separators
Incorporate graphene, carbon nanotubes, or other nanomaterials to improve ion transport and mechanical properties.
Emerging technology for nextgeneration batteries.
●Advantages of Battery Separators
1. Safety Enhancement
Prevents short circuits and thermal runaway, ensuring safe operation.
2. Improved Performance
Optimizes ion transport and reduces internal resistance, leading to better efficiency.
3. Longevity
Protects the electrodes from degradation, extending the battery's lifespan.
4. Versatility
Suitable for various battery chemistries, including lithiumion, nickelmetal hydride (NiMH), and leadacid.
5. CostEffectiveness
Mass production of polymeric separators makes them affordable for widespread use.
●Challenges in Battery Separator Technology
1. Thermal Management
High temperatures can cause shrinkage or melting of some separators, leading to failure.
2. Dendrite Growth
Lithium dendrites can penetrate the separator, causing internal shorts and safety hazards.
3. Wettability
Poor wettability by the electrolyte can hinder ion transport and reduce performance.
4. Environmental Impact
Disposal of nonbiodegradable separators poses environmental concerns.
5. Manufacturing Complexity
Producing advanced separators with uniform porosity and thickness can be challenging.
●Innovations in Battery Separator Technology
To address these challenges and enhance performance, researchers and manufacturers are developing cuttingedge separator technologies:
1. Smart Separators
Incorporate sensors to monitor temperature, pressure, and other parameters in realtime for predictive maintenance.
2. SelfHealing Materials
Use polymers or nanomaterials capable of repairing small defects to prevent catastrophic failures.
3. GrapheneBased Separators
Leverage graphene's exceptional mechanical strength and conductivity to create ultrathin, highperformance separators.
4. Biodegradable Materials
Develop environmentally friendly separators made from natural or renewable resources.
5. SolidState Separators
Explore solid electrolytes as alternatives to liquidbased separators for safer and more energydense batteries.
●Applications of Battery Separators
Battery separators are used across a wide range of industries and applications:
1. Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Ensure safe and efficient operation of highcapacity lithiumion batteries in EVs.
2. Consumer Electronics
Enable compact and reliable batteries for smartphones, laptops, and other portable devices.
3. Renewable Energy Systems
Facilitate energy storage in solar panels, wind turbines, and gridscale systems.
4. Medical Devices
Power implantable devices and diagnostic equipment where reliability and safety are paramount.
5. Industrial Applications
Support heavyduty batteries for backup power, telecommunications, and transportation.
●The Future of Battery Separator Technology
As battery technology continues to evolve, so too will the separators that enable their performance. Key trends shaping the future include:
1. Increased Efficiency
Development of thinner, more conductive separators to maximize energy density.
2. Focus on Safety
Enhanced thermal stability and puncture resistance to prevent catastrophic failures.
3. Integration with Emerging Technologies
Combining separators with solidstate electrolytes and nanomaterials for nextgeneration batteries.
4. Sustainability
Greater emphasis on using biodegradable and recyclable materials to reduce environmental impact.
5. Global Standards Compliance
Ensuring compatibility with evolving international regulations for battery components.
●Conclusion
Battery separators are a critical component in modern energy storage systems, ensuring safe and efficient electrochemical reactions. Their unique combination of electrical insulation, ion conduction, and mechanical strength makes them indispensable in a wide range of applications.
What excites you most about the advancements in battery separator technology? Share your thoughts below! Together, let’s explore how these innovative materials can shape the future of energy storage and sustainability.
 English▼
English▼





 +86 13174506016
+86 13174506016 David@tmaxcn.com
David@tmaxcn.com

